Overview:-
TMM is a mathematical technique used in higher dimensional statistical mechanics problems. In engineering, systems are represented in form of Matrices. Often complex structures have multiple sub-structures embedded in it. This increases the dimension of the model. To tap the behaviour of each member and to translate it to the final behaviour of the system overall, we need to solve such higher dimension models. Such models can quickly become too complex to solve even by the computers. Hence techniques like Transfer Matrix method can write the partition functions into simpler forms. TMM can be used in problems where we are analysis the frequency of a composite structure; like a composite cantilever beam having multiple layers of material. Rayleigh-Ritz method is an another useful Energy based technique which works based on variational calculus and utilizes superpositioned shape function to converge to accurate frequency values.
Parameters in analysis:-
- Boundary conditions assumed :- fixed-pinned
- Steel Beam substrate of dimensions 300mm x 20mm x 1mm. Brass Piezo patch attached on beam substrate at 70mm from clamped end (dimensions: 40mm x 20mm x 1.5mm).
- Standard linear properties are taken for Brass and Steel material.
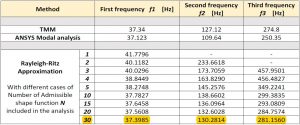
Result:-
ANSYS Modal analysis, TMM, and Rayleigh-Ritz approximation methods were compared for the frequency values. From the table given below, TMM seems to be the most accurate method followed by Rayleigh-Ritz & ANSYS modal method. The error in Rayleigh-Ritz is apparent because the method does not truely models the structure mthematically and relies on superposition of several approximate lagrange shape functions to converge to results.
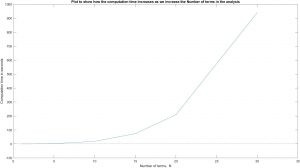
In Rayleigh-Ritz method, we find that upon increasing the number of superimposed shape function terms, the result is refined even more, however, computation time increases exponentially as seen in the graph. But including more number of terms will not refine the results after a certain extent. Therefore, the optimum number of terms that were determined were 30 ~ 35 with a maximum computation time of 15 minutes.